My outreach activities consist of several efforts (1) public talks, (2) mentoring young students, and (3) interactions with visual artists/scientific visualization. Below are several visual projects that were published or shown publicly as part of outreach programs. | ||
Atlanta's Science.Art.Wonder 2021-2022 |
||
|
||
|
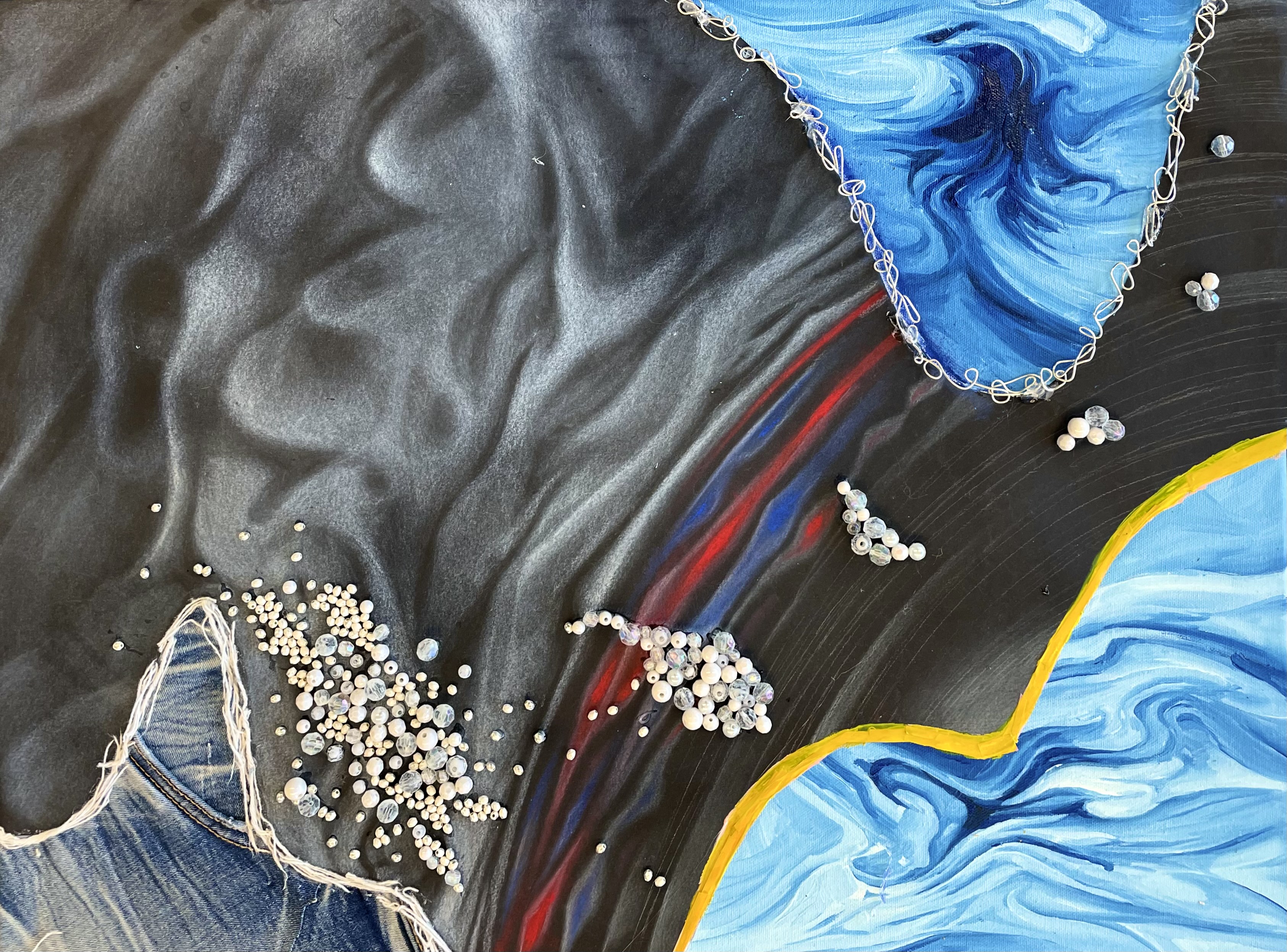
It is a mixed media piece called "Flow Dance" by Choux Kim, and was shown as part of several art shows in the Atlanta area (including at Georgia Tech and the Atlanta Science Festival) in spring 2022. |
||
Atlanta's Science.Art.Wonder 2020-2021 |
||
|
||
|
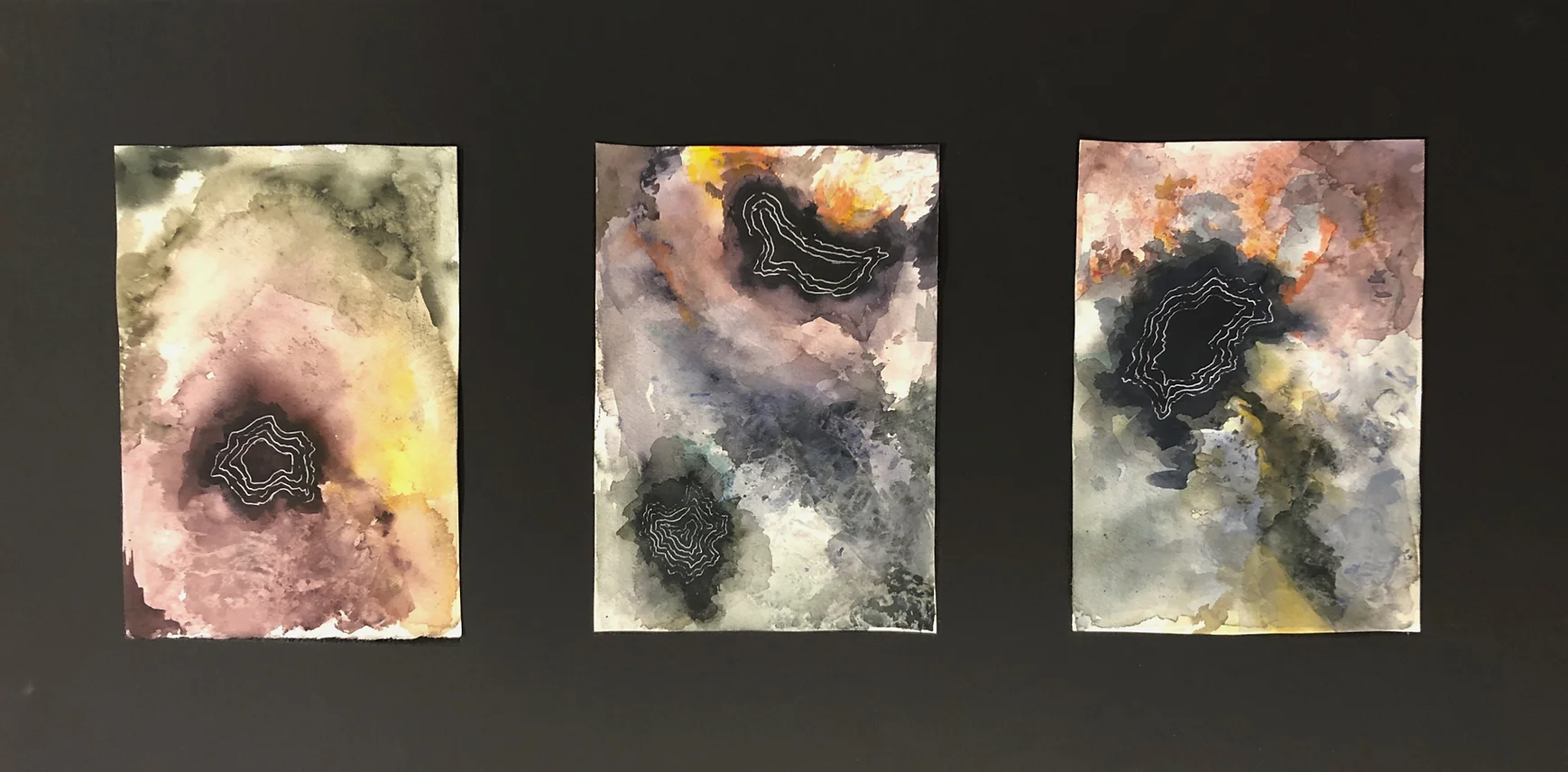
It is a series of watercolor paintings called "Astro Fluids," produced by Sofia Mendoza Lomeli, and was shown as part of several art shows in the Atlanta area in spring 2021. |
||
2017 Images of Research at the University of Exeter |
||
|
||
|
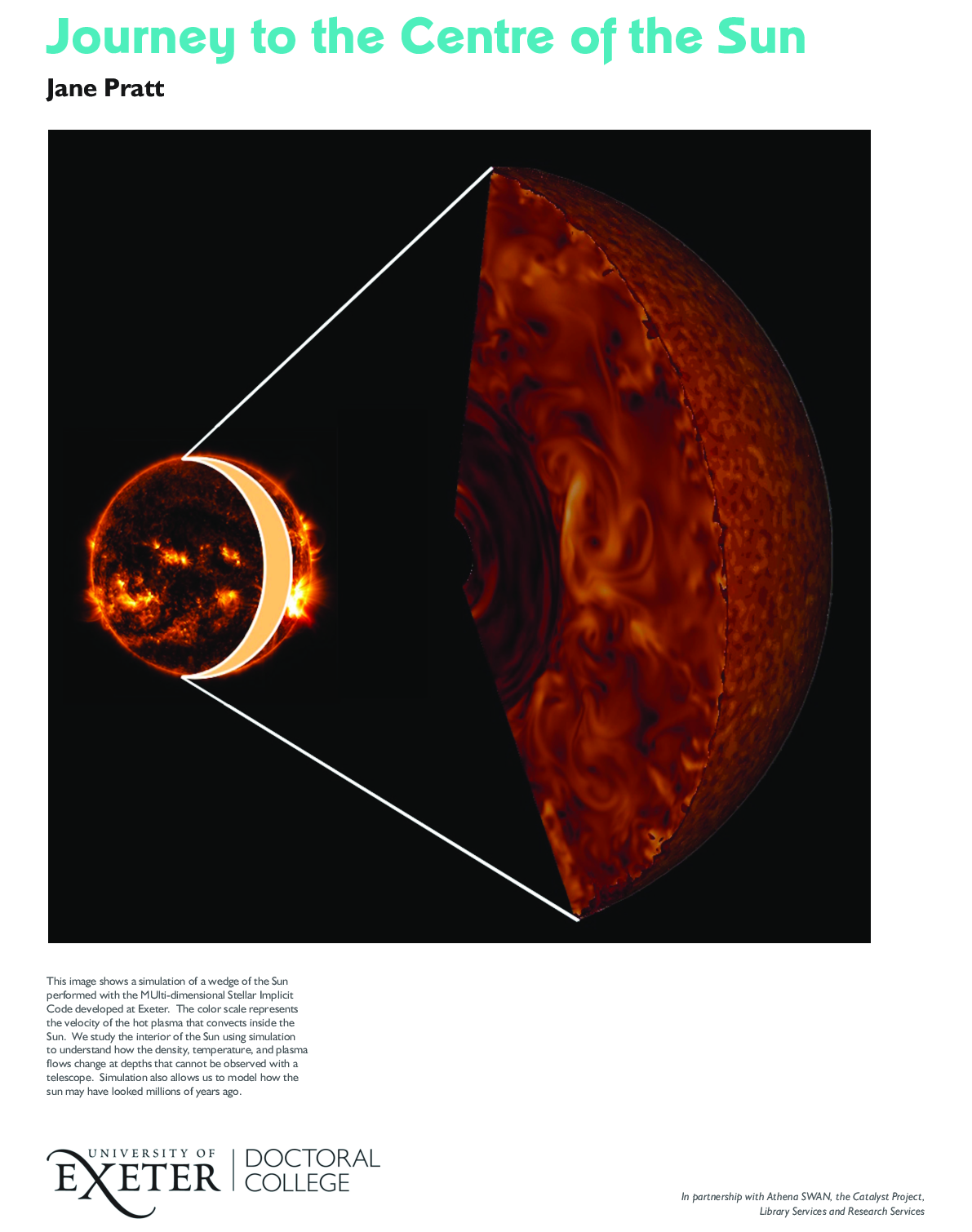
Title: Journey to the Centre of the Sun. Narrative: This image shows a simulation of a wedge of the Sun performed with the MUlti-dimensional Stellar Implicit Code developed at Exeter. The color scale represents the velocity of the hot plasma that convects inside the Sun. We study the interior of the Sun using simulation to understand how the density, temperature, and plasma flows change at depths that cannot be observed with a telescope. Simulation also allows us to model how the sun may have looked millions of years ago. |
||
2017 Images of Research at the University of Exeter |
||
|
||
|
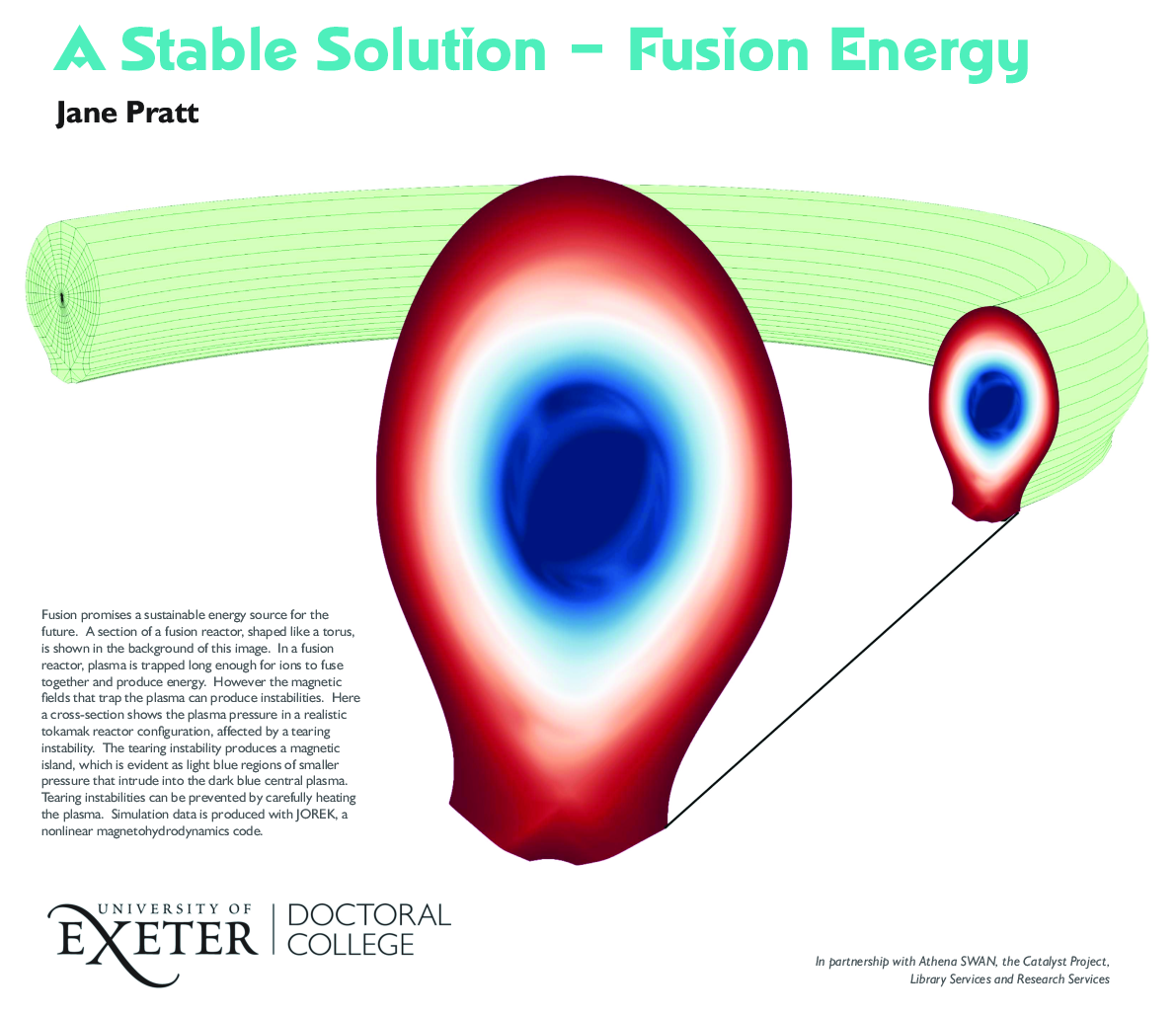
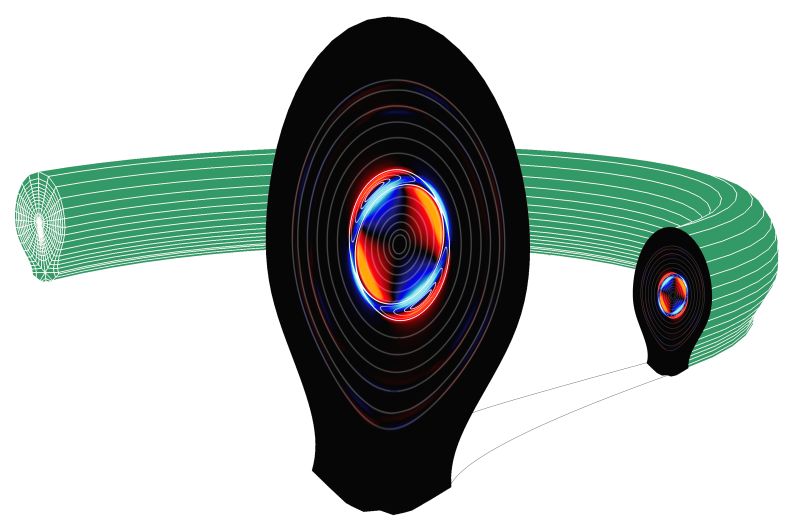
Title: "A Stable Solution – Fusion Energy." Narrative: Fusion promises a sustainable energy source for the future. A section of a fusion reactor, shaped like a torus, is shown in the background of this image. In a fusion reactor, plasma is trapped long enough for ions to fuse together and produce energy. However the magnetic fields that trap the plasma can produce instabilities. Here a cross-section shows the plasma pressure in a realistic tokamak reactor configuration, affected by a tearing instability. The tearing instability produces a magnetic island, which is evident as light blue regions of smaller pressure that intrude into the dark blue central plasma. Tearing instabilities can be prevented by carefully heating the plasma. Simulation data is produced with JOREK, a nonlinear magnetohydrodynamics code. |
||
2016 Images of Research at the University of Exeter |
||
|
||
|
This image was judged and won a "Highly Commended" in the 2016 Images of Research at UoE. (See the poster here.) Title: "Elegant Chaos: Supercomputing Turbulence." Narrative: This image shows the colorful connecting wires in the back of a Cray XC30 supercompter. Superimposed is a visualization of a turbulent plasma from a simulation performed on this computer. Plasmas are formed by heating a gas until it is completely ionized. When it is very hot, the plasma flow becomes turbulent. Magnetic fields change the way the plasma moves. Understanding the fundamentals of turbulence in plasmas is key both to achieving fusion energy and to protecting earth and our satellites from solar storms. |
||
2016 ARCHER Image Calendar |
||
|
||
|
ARCHER, the UK National Supercomputing Service, has an annual image contest and produces a calendar with the winning images. The images in the 2016 calendar can be viewed here. Title: "Harnessing the power of the Sun: Magnetic reconnection in a cross-section of a realistic tokamak simulated with the JOREK code." Narrative: Fusion is a process that heats the Sun and stars. If harnessed in the future, fusion could generate large amounts of carbon-free energy. A tokamak, a machine that uses a magnetic field to confine the hot ionized gas that makes up a plasma, has the potential to produce energy using fusion. In a tokamak, plasma resistivity causes magnetic field lines to reconnect, forming magnetic islands. When a magnetic island grows to a large size, it can result in fast escape of plasma from the machine. This image shows a cross-section of a realistic tokamak configuration with a divertor, obtained as a snapshot from a simulation with JOREK, a nonlinear magnetohydrodynamics code. A large magnetic island is created by a perturbation of the current density which is indicated by the colours: negative current perturbations are displayed by blue colours, positive current perturbations are displayed by red colours. White lines have been plotted over the current perturbation to visualize the surfaces of constant magnetic flux. Outside of the magnetic island, these surfaces are nearly concentric. The size and position of the magnetic island is indicated by the surfaces of constant magnetic flux that form isolated pockets between the concentric circles. |
||
2015 ARCHER Image Calendar |
||
|
||
|
The images in the 2015 ARCHER calendar can be viewed here. Title: "Time-elapsed images of diffusion of tracer particles during turbulent convection." Narrative: In natural systems like stellar interiors and planetary atmospheres flows are not constrained by convection rolls or boundary layers. As well as the structure of plumes in a flow, heat transfer is highly dependent on a fluid's Prandtl number, the ratio of viscosity to thermal diffusivity. In the solar convection zone thermal diffusivity dominates, and Prandtl numbers are estimated to be 3 to 5 orders of magnitude lower than can be achieved by modern simulations. A theoretical understanding of how turbulent heat transfer changes as the Prandtl number is lowered is key to effectively modelling convection. We have developed new methods of characterizing the heat transfer in and around plumes using higher order statistics and Lagrangian tracer particles. We calculate statistics of heat transfer from pseudospectral simulations of incompressible homogeneous Boussinesq hydrodynamic convection for the wide range of Prandtl numbers. |
||